The mechanical properties of a material are those properties that involve a reaction to an applied load. The mechanical properties of metals determine the range of usefulness of a material and establish the service life that can be expected.
Mechanical properties are also used to help classify and identify material. The most common properties considered are strength, ductility, hardness, impact resistance, and fracture toughness.
Most structural materials are anisotropic, which means that their material properties vary with orientation. The variation in properties can be due to directionality in the microstructure (texture) from forming or cold working operation, the controlled alignment of fiber reinforcement and a variety of other causes.
Mechanical properties are generally specific to product form such as sheet, plate, extrusion, casting, forging, and etc. Additionally, it is common to see mechanical property listed by the directional grain structure of the material.
In products such as sheet and plate, the rolling direction is called the longitudinal direction, the width of the product is called the transverse direction, and the thickness is called the short transverse direction. The grain orientations in standard wrought forms of metallic products are shown the image.
1.1. Loading:
The application of a force to an object is known as loading. Materials can be subjected to many different loading scenarios and a material’s performance is dependent on the loading conditions.
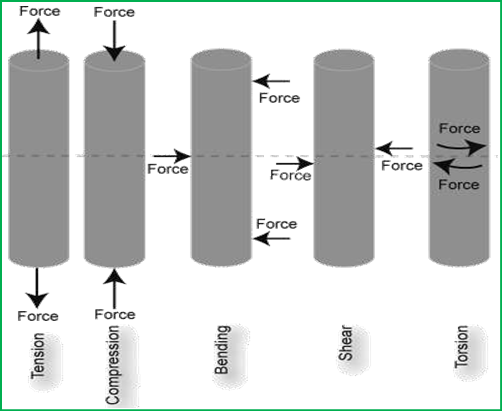
There are five fundamental loading conditions: tension, compression, bending, shear, and torsion:
Tension – is the type of loading in which the two sections of material on either side of a plane tend to be pulled apart or elongated.
Compression – is the reverse of tensile loading and involves pressing the material together. Bending – is a load in a manner that causes a material to curve and results in compressing the material on one side and stretching it on the other.
Shear – is a load parallel to a plane which caused the material on one side of the plane to want to slide across the material on the other side of the plane.
Torsion – is the application of a force that causes twisting in a material.
Static loading – is a material subjected to a constant force.
Dynamic or cyclic loading – is a not constant loading of the material, but instead fluctuates.
The way a material is loaded greatly affects its mechanical properties and largely determines how, or if, a component will fail; and whether it will show warning signs before failure actually occurs.
1.2. Stress and Strain:
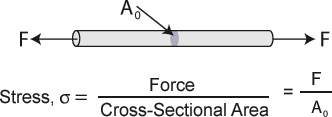
Stress – is the applied force or system of forces that tends to deform a body. The term stress is used to express the loading in terms of force applied to a certain cross-sectional area of an object.
Stress is also the internal distribution of forces within a body that balance and react to the loads applied to it. The stress distribution may or may not be uniform, depending on the nature of the loading condition.
For example, a bar loaded in pure tension will essentially have a uniform tensile stress distribution. However, a bar loaded in bending will have a stress distribution that changes with distance perpendicular to the normal axis.
The word “vector” typically refers to a quantity that has a “magnitude” and a “direction”.
For example, the stress in an axially loaded bar is simply equal to the applied force divided by the bar’s cross-sectional area.
Some common measurements of stress are:
psi = lbs./in2 (pounds per square inch);
ksi or kpsi = kilopounds/in2 (one thousand or 103 pounds per square inch);
Pa = N/m² (Pascal or Newton per square meter);
kPa = Kilopascals (one thousand or 103 Newton per square meter);
GPa = Gigapascal (one million or 106 Newton per square meter).
*Any metric prefix can be added in front of psi or Pa to indicate the multiplication factor.
We provide all types of mechanical testing services all over Tamilnadu.
Please feel free to reach us https://aqcinspection.com/training/ to learn more about any of the methods in detail.
Visit our technical and career updates at our Blog site https://advancedqualitycentre.blogspot.com . or
https://ndtcenter.blogspot.com